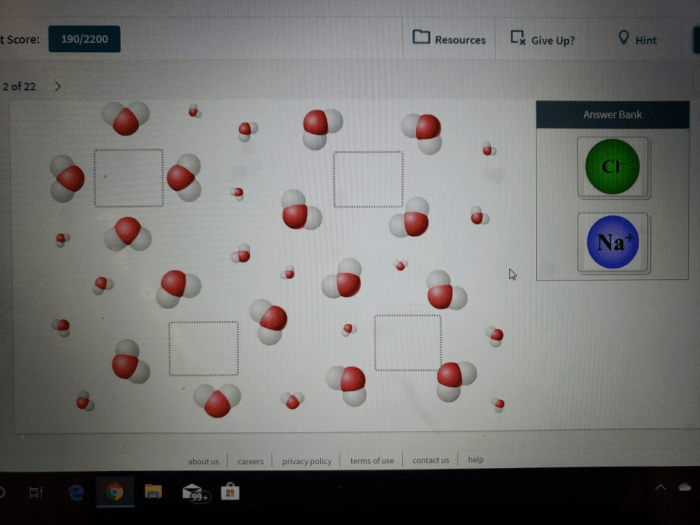
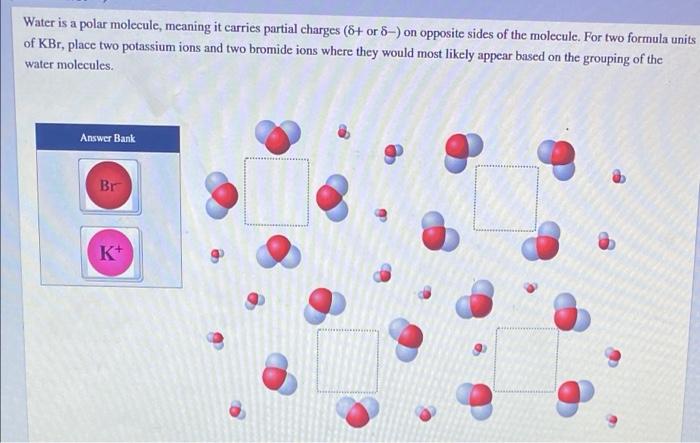
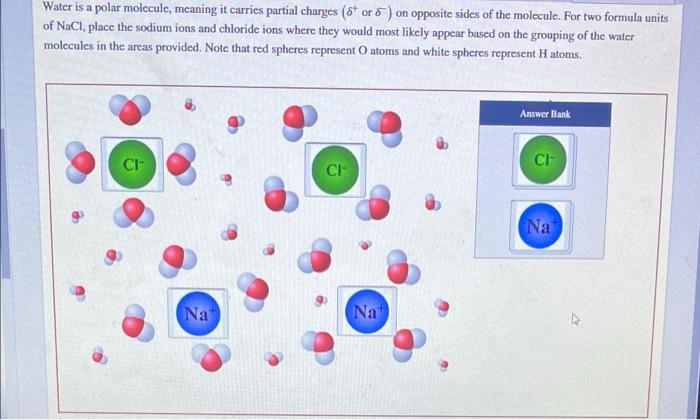
Water, a ubiquitous substance on Earth, possesses a unique molecular structure that sets it apart from many other compounds. As water is a polar molecule meaning it carries partial charges, it plays a crucial role in various biological and environmental processes.
This article delves into the polarity and partial charges of water molecules, exploring their significance and applications.
The polarity of water stems from the uneven distribution of electrons within its molecular structure, resulting in the formation of partial positive and negative charges. These partial charges contribute to water’s ability to interact with other polar molecules, forming hydrogen bonds that give water its distinctive properties.
Polarity of Water
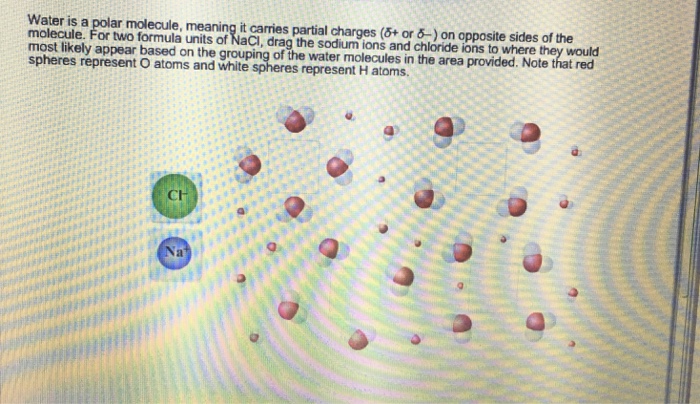
Water is a polar molecule, meaning it has a separation of electrical charges. This polarity is due to the unequal sharing of electrons between the oxygen and hydrogen atoms in the water molecule.
Polar molecules have a positive end and a negative end. The positive end of the water molecule is the hydrogen atoms, and the negative end is the oxygen atom. This polarity allows water to interact with other polar molecules and ions, making it a good solvent.
Partial Charges in Water
The partial charges in water are created by the unequal sharing of electrons between the oxygen and hydrogen atoms. The oxygen atom has a higher electronegativity than the hydrogen atoms, meaning that it attracts electrons more strongly. This results in a partial negative charge on the oxygen atom and a partial positive charge on the hydrogen atoms.
The partial charges in water contribute to its polarity and allow it to interact with other polar molecules and ions.
Hydrogen Bonding, Water is a polar molecule meaning it carries partial charges
Hydrogen bonding is a type of intermolecular force that occurs between a hydrogen atom bonded to an electronegative atom (such as oxygen, nitrogen, or fluorine) and another electronegative atom. In water, hydrogen bonding occurs between the hydrogen atoms of one water molecule and the oxygen atom of another water molecule.
Hydrogen bonds are strong and directional, and they play a major role in the unique properties of water, such as its high surface tension and high specific heat capacity.
Water’s Properties
Water’s polarity and partial charges contribute to its unique properties. These properties include:
- Surface tension:Water has a high surface tension due to the strong hydrogen bonds between water molecules.
- Specific heat capacity:Water has a high specific heat capacity due to the hydrogen bonds between water molecules. This means that it takes a lot of energy to raise the temperature of water.
- Boiling point:Water has a relatively high boiling point due to the strong hydrogen bonds between water molecules.
- Freezing point:Water has a relatively high freezing point due to the strong hydrogen bonds between water molecules.
Applications of Water’s Properties
Water’s polarity and partial charges are utilized in a variety of applications, including:
- Cleaning:Water is a good solvent for many substances, due to its polarity. This makes it useful for cleaning.
- Pharmaceuticals:Water is used as a solvent for many drugs and other pharmaceutical products.
- Agriculture:Water is essential for plant growth. It is also used to irrigate crops.
Essential FAQs: Water Is A Polar Molecule Meaning It Carries Partial Charges
What is a polar molecule?
A polar molecule is a molecule that has a separation of positive and negative charges, resulting in a net molecular dipole.
How do partial charges affect water’s properties?
Partial charges in water molecules contribute to its polarity, which influences properties such as surface tension, specific heat capacity, and boiling point.
What is the significance of hydrogen bonding in water?
Hydrogen bonding in water is responsible for its high surface tension, high specific heat capacity, and ability to dissolve many substances.