Friedel crafts alkylation of 1 4 dimethoxybenzene – The Friedel-Crafts alkylation of 1,4-dimethoxybenzene, a versatile and widely employed organic reaction, offers a powerful tool for the synthesis of complex organic molecules. This reaction, characterized by its ability to introduce alkyl groups into aromatic rings, has revolutionized the field of organic chemistry and continues to be a cornerstone of modern synthetic methodologies.
In this comprehensive exploration, we delve into the intricacies of the Friedel-Crafts alkylation of 1,4-dimethoxybenzene, examining its mechanism, substrates, reagents, reaction conditions, product formation, applications, and safety considerations. By unraveling the complexities of this reaction, we aim to empower chemists with a deeper understanding of its utility and enable them to harness its potential for groundbreaking discoveries.
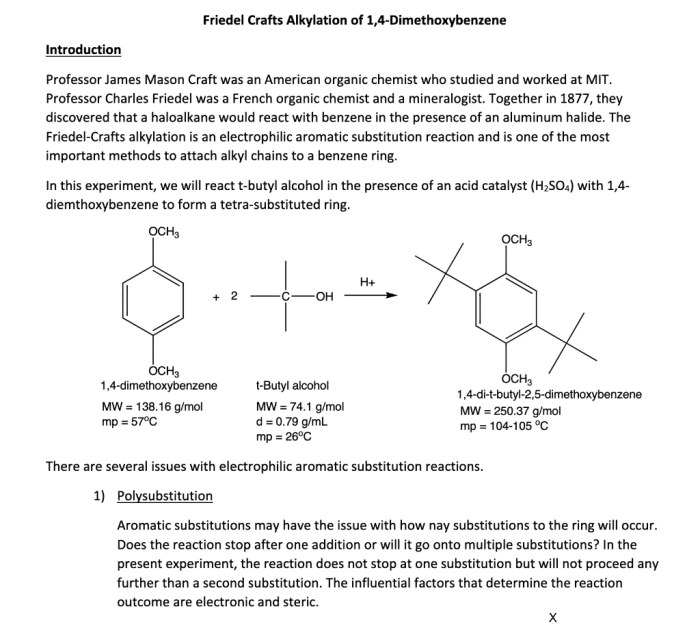
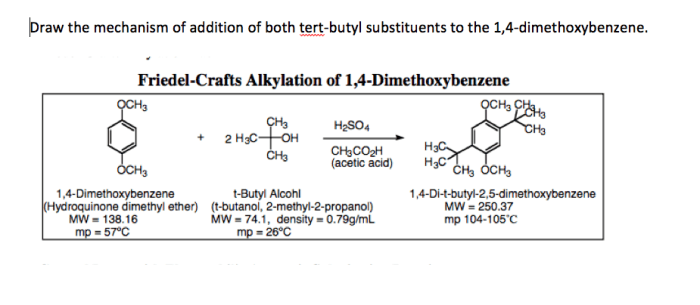
Friedel-Crafts Alkylation of 1,4-Dimethoxybenzene
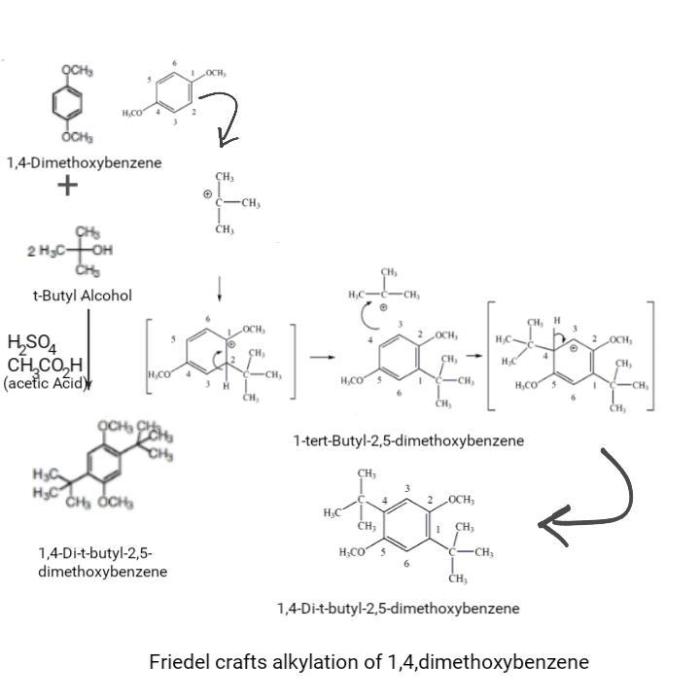
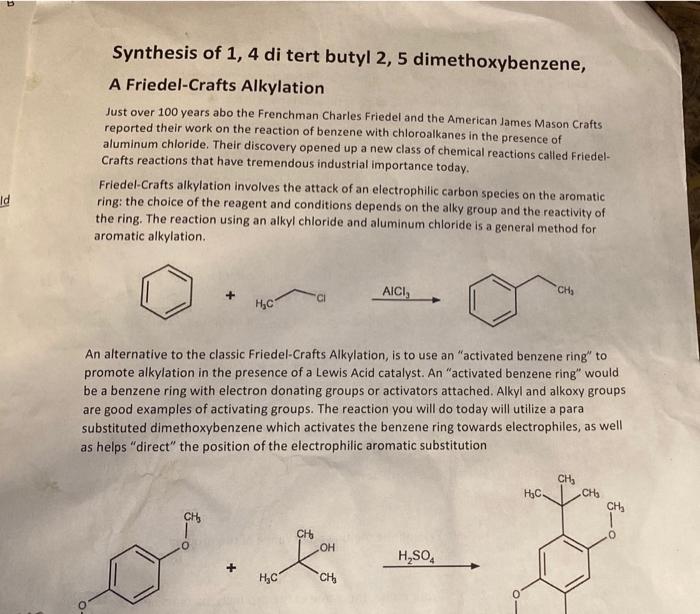
Friedel-Crafts alkylation is a versatile reaction in organic chemistry that involves the alkylation of aromatic compounds using alkyl halides in the presence of a Lewis acid catalyst. This reaction is widely used in the synthesis of a variety of organic compounds, including pharmaceuticals, dyes, and fragrances.
The mechanism of the Friedel-Crafts alkylation reaction proceeds through the formation of a carbocation intermediate, which is then attacked by the aromatic ring. The Lewis acid catalyst activates the alkyl halide, making it more susceptible to nucleophilic attack by the aromatic ring.
Substrates and Reagents
The substrates used in the Friedel-Crafts alkylation of 1,4-dimethoxybenzene are typically alkyl halides and 1,4-dimethoxybenzene. The alkyl halides can be primary, secondary, or tertiary, and the 1,4-dimethoxybenzene can be substituted with a variety of functional groups.
The reactivity of the alkyl halides depends on the stability of the carbocation intermediate. Primary alkyl halides are the most reactive, followed by secondary alkyl halides, and then tertiary alkyl halides. The selectivity of the reaction depends on the steric and electronic effects of the substituents on the aromatic ring.
Reaction Conditions
The Friedel-Crafts alkylation of 1,4-dimethoxybenzene is typically carried out in a solvent such as dichloromethane or nitrobenzene. The reaction temperature is typically between 0 and 50 °C, and the reaction time can vary from a few hours to several days.
The choice of Lewis acid catalyst can have a significant effect on the reaction rate and selectivity. Common Lewis acid catalysts include aluminum chloride, iron(III) chloride, and zinc chloride.
Product Formation
The products of the Friedel-Crafts alkylation of 1,4-dimethoxybenzene are typically alkylated 1,4-dimethoxybenzenes. The regioselectivity of the reaction depends on the steric and electronic effects of the substituents on the aromatic ring.
The stereoselectivity of the reaction depends on the nature of the alkyl halide. Primary alkyl halides typically give a mixture of enantiomers, while secondary and tertiary alkyl halides typically give a single enantiomer.
Applications
The Friedel-Crafts alkylation of 1,4-dimethoxybenzene is a versatile reaction that can be used to synthesize a variety of organic compounds. This reaction is used in the synthesis of pharmaceuticals, dyes, and fragrances.
One example of the use of the Friedel-Crafts alkylation of 1,4-dimethoxybenzene is the synthesis of the drug ibuprofen. Ibuprofen is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug that is used to treat pain, fever, and inflammation.
Safety Considerations, Friedel crafts alkylation of 1 4 dimethoxybenzene
The Friedel-Crafts alkylation of 1,4-dimethoxybenzene is a hazardous reaction that should be carried out with caution. The alkyl halides and Lewis acid catalysts used in this reaction are corrosive and toxic.
The following guidelines should be followed when carrying out the Friedel-Crafts alkylation of 1,4-dimethoxybenzene:
- Wear appropriate personal protective equipment, including gloves, goggles, and a lab coat.
- Carry out the reaction in a well-ventilated area.
- Handle the alkyl halides and Lewis acid catalysts with care.
- Dispose of the reaction products and waste materials properly.
Question Bank: Friedel Crafts Alkylation Of 1 4 Dimethoxybenzene
What are the advantages of using 1,4-dimethoxybenzene in Friedel-Crafts alkylation reactions?
1,4-Dimethoxybenzene offers several advantages in Friedel-Crafts alkylation reactions. Its electron-rich nature enhances the reactivity of the aromatic ring towards electrophiles, facilitating the alkylation process. Additionally, the presence of methoxy groups provides steric hindrance, directing the alkylation to occur predominantly at the para position, leading to regioselectivity in product formation.
How does the choice of catalyst influence the outcome of the Friedel-Crafts alkylation of 1,4-dimethoxybenzene?
The choice of catalyst plays a crucial role in the Friedel-Crafts alkylation of 1,4-dimethoxybenzene. Lewis acids, such as aluminum chloride (AlCl3) and iron(III) chloride (FeCl3), are commonly employed as catalysts. The catalyst activates the alkylating agent, forming an electrophile that readily reacts with the aromatic ring.
The strength and nature of the catalyst can affect the reaction rate, regioselectivity, and stereoselectivity of the alkylation process.
What are the safety considerations associated with the Friedel-Crafts alkylation of 1,4-dimethoxybenzene?
The Friedel-Crafts alkylation of 1,4-dimethoxybenzene involves the use of hazardous chemicals, including alkylating agents and Lewis acid catalysts. Proper safety precautions must be taken to minimize the risks associated with these chemicals. Adequate ventilation, protective clothing, and appropriate disposal methods are essential to ensure a safe working environment.