Which of the choices is an example of offshore outsourcing? This question delves into the intricacies of a business strategy that has gained significant traction in recent times. Offshore outsourcing involves contracting services or tasks to third-party providers located in different countries, often with the aim of reducing costs and accessing specialized expertise.
This practice has proliferated across various industries, leading to a diverse range of offshore outsourcing examples. From software development to customer support, companies are increasingly leveraging this approach to enhance their operations and gain a competitive edge.
Definition of Offshore Outsourcing

Offshore outsourcing refers to the practice of contracting a service or business process to a third-party provider located in a foreign country. This involves transferring specific tasks or functions to an external organization that operates in a different geographical location, typically with the goal of reducing costs and improving efficiency.
Examples of offshore outsourcing include:
- Software development and maintenance
- Customer service and support
- Data entry and processing
- Accounting and finance
- Research and development
The benefits of offshore outsourcing can include:
- Cost savings due to lower labor costs in other countries
- Access to a wider pool of skilled workers
- Improved efficiency and productivity
- Focus on core competencies
Types of Offshore Outsourcing: Which Of The Choices Is An Example Of Offshore Outsourcing

There are different types of offshore outsourcing based on the nature of the services or processes outsourced:
- Business Process Outsourcing (BPO):Involves outsourcing non-core business functions such as customer service, payroll processing, or data entry.
- Information Technology Outsourcing (ITO):Focuses on outsourcing IT-related services such as software development, infrastructure management, or cloud computing.
- Knowledge Process Outsourcing (KPO):Involves outsourcing knowledge-intensive tasks such as research, analysis, or legal services.
- Manufacturing Outsourcing:Entails outsourcing production or manufacturing processes to a foreign country.
- Project-Based Outsourcing:Involves outsourcing specific projects or tasks on a temporary or contractual basis.
Considerations for Offshore Outsourcing
When considering offshore outsourcing, several factors should be taken into account:
- Cost-benefit analysis:Evaluating the potential cost savings and benefits against the risks and challenges.
- Provider selection:Conducting thorough research and due diligence to identify reputable and reliable outsourcing partners.
- Cultural and language differences:Understanding and addressing potential communication barriers and cultural nuances.
- Data security and privacy:Ensuring compliance with relevant regulations and implementing robust data protection measures.
- Intellectual property protection:Safeguarding intellectual property rights and confidential information.
Risks and challenges associated with offshore outsourcing include:
- Quality control:Maintaining quality standards and ensuring consistency in outsourced processes.
- Communication challenges:Overcoming language barriers, time zone differences, and cultural misunderstandings.
- Data security breaches:Mitigating risks of data breaches and unauthorized access to sensitive information.
- Legal and regulatory compliance:Navigating different legal and regulatory frameworks across jurisdictions.
- Dependence on third-party providers:Managing the risks associated with relying on external organizations for critical services.
To mitigate risks and overcome challenges, strategies include:
- Establishing clear contracts:Outlining expectations, performance metrics, and dispute resolution mechanisms.
- Regular monitoring and evaluation:Tracking performance, identifying areas for improvement, and ensuring compliance.
- Building strong relationships:Fostering open communication, collaboration, and trust with outsourcing partners.
- Investing in technology:Utilizing technology to enhance communication, streamline processes, and improve data security.
- Developing contingency plans:Preparing for potential disruptions or unexpected events to minimize impact on operations.
Examples of Offshore Outsourcing
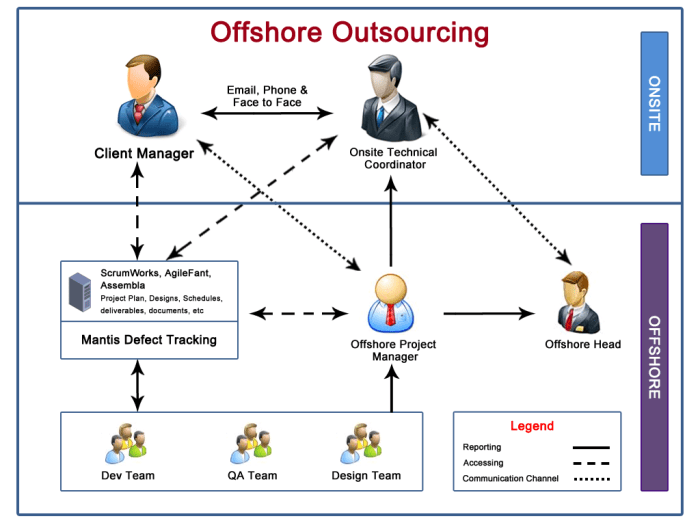
Examples of offshore outsourcing in various industries include:
- Banking:Outsourcing customer service, data processing, and software development to India and the Philippines.
- Manufacturing:Outsourcing production of goods to countries like China, Vietnam, and Mexico.
- Healthcare:Outsourcing medical transcription, data entry, and billing services to India and the Philippines.
- Technology:Outsourcing software development, cloud computing, and infrastructure management to India and Eastern Europe.
- Retail:Outsourcing customer service, order fulfillment, and logistics to India and the Philippines.
The reasons for choosing offshore outsourcing in these cases include:
- Cost savings:Lower labor costs in offshore locations.
- Access to skilled labor:Availability of skilled workers with specific expertise in certain regions.
- Improved efficiency:Streamlining processes and leveraging economies of scale.
- Focus on core competencies:Allowing companies to focus on their core strengths and strategic initiatives.
The outcomes and benefits of these offshore outsourcing projects have been:
- Reduced operating costs:Significant savings on labor and overhead expenses.
- Improved customer satisfaction:Enhanced customer service through 24/7 support and reduced wait times.
- Increased efficiency:Streamlined processes and automation leading to faster turnaround times.
- Innovation:Access to a wider pool of skilled workers and exposure to new technologies.
- Competitive advantage:Enhanced competitiveness through cost savings and improved service delivery.
Trends in Offshore Outsourcing

Emerging trends in offshore outsourcing include:
- Digital transformation:Outsourcing services related to cloud computing, data analytics, and artificial intelligence.
- Automation and AI:Increasing use of automation and artificial intelligence to streamline processes and reduce costs.
- Geographic diversification:Expansion of outsourcing to new locations beyond traditional offshore destinations.
- Vertical specialization:Focus on outsourcing specific industry-specific services, such as healthcare outsourcing or legal outsourcing.
- Sustainability:Increasing consideration of environmental and social sustainability factors in offshore outsourcing decisions.
Factors driving these trends include:
- Technological advancements:Digital transformation and automation enabling new possibilities for outsourcing.
- Global competition:Increased pressure to reduce costs and improve efficiency.
- Skilled labor shortage:Growing demand for skilled workers in certain industries and regions.
- Globalization:Increased interconnectedness and ease of doing business across borders.
- Sustainability concerns:Growing awareness of the environmental and social impact of business practices.
The potential impact of these trends on the future of offshore outsourcing includes:
- Increased adoption:Offshore outsourcing becoming more prevalent across industries and business functions.
- Greater sophistication:Outsourcing evolving from basic services to more complex and specialized tasks.
- New opportunities:Emerging technologies and trends creating new opportunities for offshore outsourcing providers.
- Sustainability focus:Offshore outsourcing becoming more sustainable and ethical.
- Competitive advantage:Companies leveraging offshore outsourcing to gain a competitive edge in the global marketplace.
Question Bank
What are the key benefits of offshore outsourcing?
Offshore outsourcing offers several advantages, including reduced labor costs, access to specialized skills, increased efficiency, and enhanced flexibility.
What are some common challenges associated with offshore outsourcing?
Potential challenges include communication barriers, cultural differences, data security concerns, and managing quality control.
How can businesses mitigate the risks of offshore outsourcing?
To minimize risks, businesses should conduct thorough due diligence, establish clear contracts, foster effective communication, and implement robust monitoring and evaluation processes.