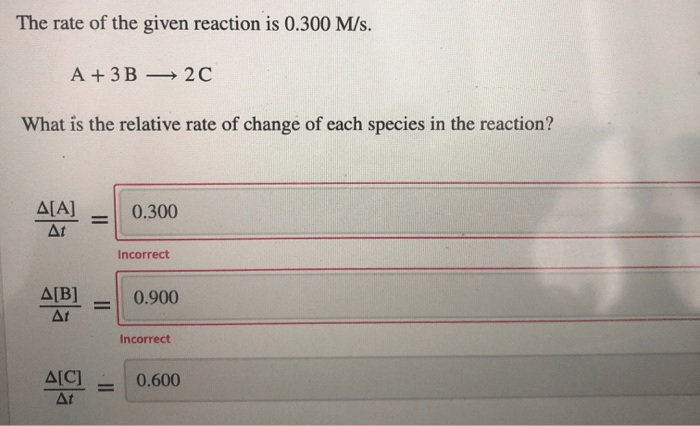
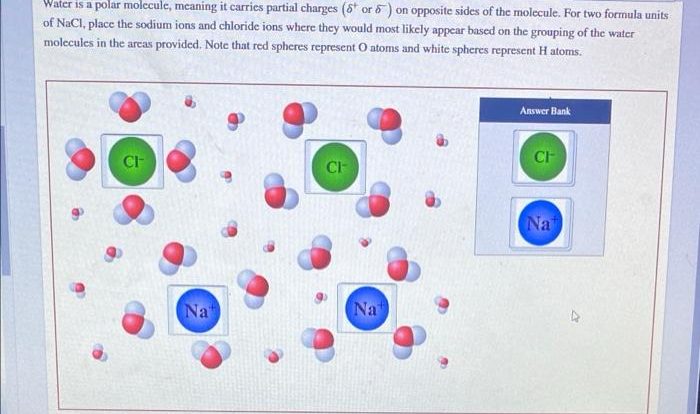
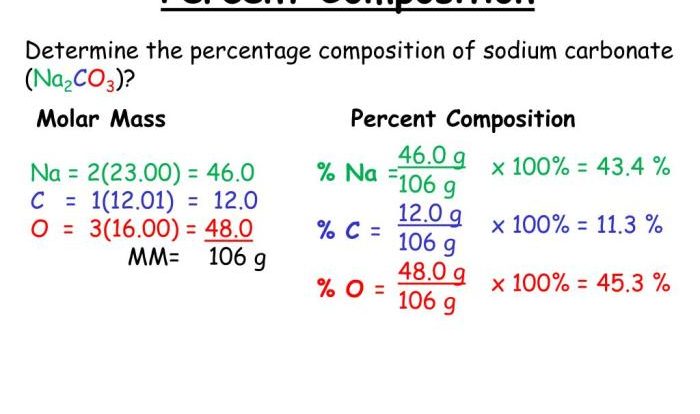
The rate of the given reaction is 0.420 m/s – The rate of a chemical reaction is a crucial concept in chemistry, providing insights into the dynamics and behavior of chemical processes. The rate of the given reaction, measured at 0.420 m/s, offers a fascinating glimpse into the factors influencing reaction kinetics and their practical applications.
Reaction rate, expressed in units of molarity per second (M/s), quantifies the change in concentration of reactants or products over time. Understanding the factors that affect reaction rate, such as concentration, temperature, surface area, and catalysts, enables chemists to manipulate and control chemical reactions for various purposes.
Rate of Reaction
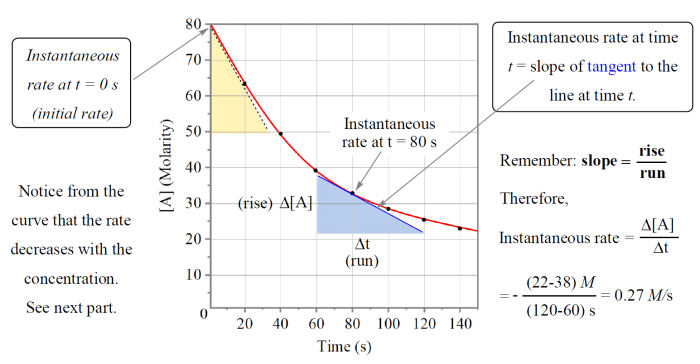
The rate of reaction refers to the change in concentration of reactants or products over time. It quantifies the speed at which a chemical reaction proceeds. The rate of reaction is typically measured in units of moles per liter per second (M/s).
Factors Affecting Reaction Rate, The rate of the given reaction is 0.420 m/s
- Concentration: The rate of reaction increases as the concentration of reactants increases. This is because there are more reactants available to collide and react with each other.
- Temperature: The rate of reaction increases as the temperature increases. This is because the higher the temperature, the more energy the reactants have, which makes it more likely that they will collide with enough energy to react.
- Surface Area: The rate of reaction increases as the surface area of the reactants increases. This is because the larger the surface area, the more reactants are exposed to each other and can react.
- Catalysts: Catalysts are substances that increase the rate of reaction without being consumed in the reaction. They do this by providing an alternative pathway for the reaction to occur, which lowers the activation energy and makes it more likely that the reactants will react.
Measuring Reaction Rate
- Spectrophotometry: This method involves measuring the change in absorbance of light by the reactants or products over time. The absorbance is directly proportional to the concentration of the substance, so the rate of reaction can be determined by measuring the change in absorbance over time.
- Gas Chromatography: This method involves separating the reactants and products based on their different boiling points. The rate of reaction can be determined by measuring the change in the concentration of the reactants or products over time.
- Titration: This method involves adding a known concentration of a reagent to the reaction mixture until the reaction is complete. The rate of reaction can be determined by measuring the volume of reagent added over time.
Applications of Reaction Rate
- Chemical Engineering: The rate of reaction is important in chemical engineering for designing reactors and optimizing reaction conditions.
- Medicine: The rate of reaction is important in medicine for understanding the effects of drugs and designing new therapies.
- Environmental Science: The rate of reaction is important in environmental science for understanding the fate of pollutants and designing strategies to mitigate their effects.
Query Resolution: The Rate Of The Given Reaction Is 0.420 M/s
What is the significance of reaction rate in chemistry?
Reaction rate provides insights into the speed and efficiency of chemical processes, allowing chemists to predict and control the outcome of reactions.
How does temperature influence reaction rate?
Increasing temperature generally increases reaction rate by providing more energy to reactant molecules, enabling them to overcome activation barriers.
What is the role of catalysts in reaction rate?
Catalysts are substances that enhance reaction rates without being consumed, providing alternative pathways with lower activation energies.