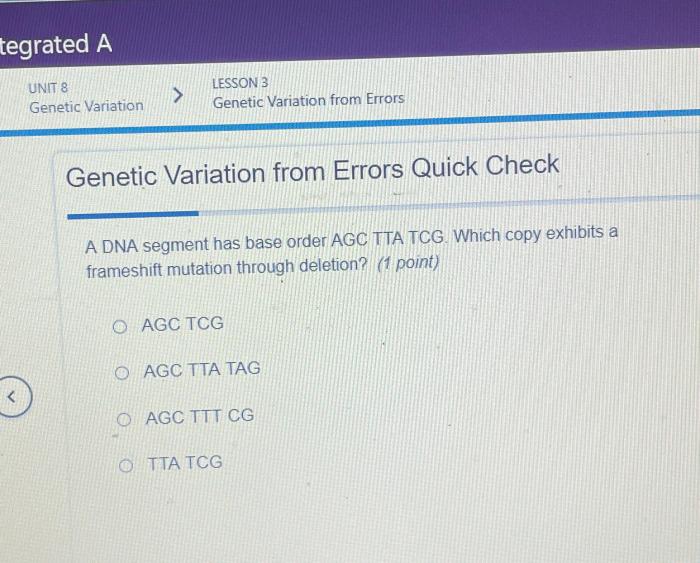
A dna segment has base order agc tta tcg – The DNA segment with base order AGC TTA TCG holds a wealth of genetic information, offering a fascinating glimpse into the intricacies of life. As we embark on this exploration, we will unravel the secrets encoded within this specific sequence, delving into the fundamental concepts of DNA structure, function, and its profound impact on biological processes.
This segment, composed of the nucleotides adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C), and thymine (T), forms the building blocks of DNA, the molecule that carries the genetic instructions for all living organisms. Understanding the arrangement and composition of these bases is crucial for deciphering the genetic code and unlocking the mysteries of heredity.
DNA Sequence Analysis
DNA sequencing is a technique used to determine the order of nucleotides in a DNA molecule. It plays a vital role in various fields, including genetics, medicine, and forensics. The Sanger sequencing method, developed by Frederick Sanger, is a widely used technique that involves the use of dideoxynucleotides to terminate DNA synthesis.
Significance of DNA Sequence Analysis
- Identification of genetic variations and mutations
- Diagnosis and treatment of genetic diseases
- Phylogenetic studies and evolutionary analysis
- Forensic investigations and paternity testing
Nucleotide Composition

DNA is composed of four types of nucleotides: adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G), and thymine (T). These nucleotides pair with each other according to specific rules: A with T, and C with G. The base pairing rules determine the structure and stability of the DNA molecule.
Importance of Nucleotide Composition
- Stability and structural integrity of DNA
- Recognition and binding sites for proteins and enzymes
- Transcriptional regulation and gene expression
Transcription and Translation
Transcription is the process of synthesizing an RNA molecule from a DNA template. The resulting RNA molecule, known as messenger RNA (mRNA), carries the genetic information from the nucleus to the cytoplasm. Translation is the process of synthesizing a protein from an mRNA template.
Ribosomes, along with transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules, facilitate the translation process.
Importance of Transcription and Translation
- Gene expression and protein synthesis
- Regulation of cellular processes
- Development and differentiation of cells
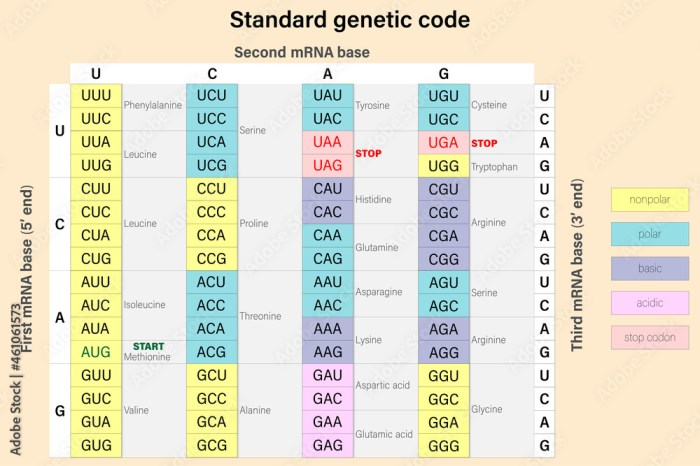
Genetic Code
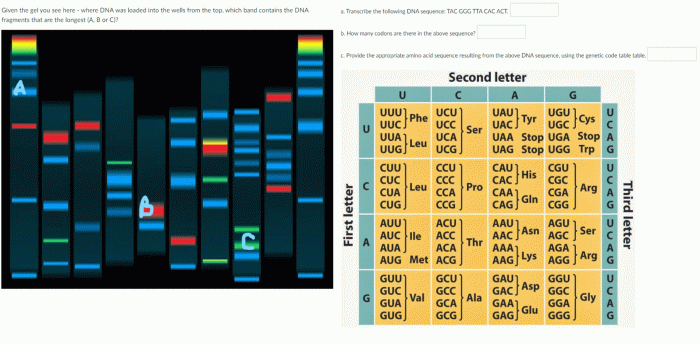
The genetic code is a set of rules that governs the relationship between the sequence of nucleotides in DNA and the sequence of amino acids in proteins. Each codon, consisting of three nucleotides, specifies a particular amino acid or a stop signal.
The genetic code is universal, meaning it is the same across all living organisms.
Table of the Genetic Code
| Codon | Amino Acid |
|---|---|
| UUU, UUC | Phenylalanine |
| UUA, UUG | Leucine |
| … | … |
Mutations
Mutations are changes in the DNA sequence that can occur spontaneously or be induced by environmental factors. Mutations can be classified into different types based on their size and effect on gene function.
Types of Mutations
- Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs)
- Insertions and deletions
- Copy number variations (CNVs)
- Chromosomal rearrangements
Potential Effects of Mutations, A dna segment has base order agc tta tcg
- Alteration of protein function
- Loss of gene function
- Gain of new gene function
- Phenotypic changes in the organism
DNA Replication
DNA replication is the process of copying the DNA molecule to create two identical copies. It is essential for cell division and the transmission of genetic information to daughter cells. DNA polymerase, an enzyme, plays a crucial role in the replication process.
Importance of DNA Replication
- Cell division and growth
- Maintenance of genetic information
- Repair of damaged DNA
Query Resolution: A Dna Segment Has Base Order Agc Tta Tcg
What is the significance of DNA sequence analysis?
DNA sequence analysis enables the identification of genetic variations, disease-causing mutations, and the development of personalized medicine.
How does nucleotide composition influence DNA structure?
The ratio of purines (A and G) to pyrimidines (C and T) affects the stability and flexibility of the DNA double helix.
What is the role of the genetic code in protein synthesis?
The genetic code provides the instructions for translating DNA sequences into specific amino acid sequences, which determine the structure and function of proteins.