Embarking on a journey into the realm of algebra, we present the Point Slope Form Worksheet Algebra 1, a meticulously crafted resource designed to illuminate the intricacies of this fundamental concept. Through a blend of theoretical explanations, practical examples, and engaging practice problems, this worksheet empowers students to master the art of point-slope form.
Delving into the essence of point-slope form, we explore its relationship with slope-intercept form, unlocking the ability to seamlessly convert between these two representations. Real-world applications are brought to life, demonstrating the practical significance of point-slope form in everyday scenarios.
Point-Slope Form Definition
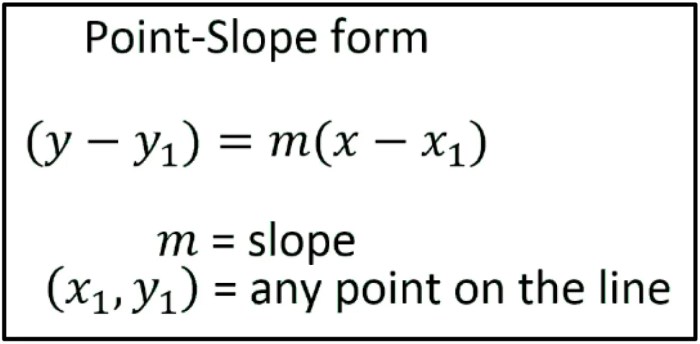
The point-slope form of a linear equation is a mathematical equation that describes a straight line using a specific point and the slope of the line.
The equation of a line in point-slope form is given by:
y
- y1= m(x
- x 1)
where:
- (x 1, y 1) is a point on the line
- m is the slope of the line
Slope-Intercept Form and Point-Slope Form
The slope-intercept form of a linear equation is another way to represent a straight line. The equation of a line in slope-intercept form is given by:
y = mx + b
where:
- m is the slope of the line
- b is the y-intercept of the line
The point-slope form and the slope-intercept form of a linear equation are equivalent. You can convert from one form to the other by solving for y.
Applications of Point-Slope Form
Point-slope form is useful for finding the equation of a line when you know a point on the line and the slope of the line. For example, if you know that a line passes through the point (2, 3) and has a slope of 2, then the equation of the line in point-slope form is:
y
- 3 = 2(x
- 2)
Point-slope form can also be used to find the equation of a line that is parallel or perpendicular to a given line. For example, if you know that a line is parallel to the line y = 2x + 1, then the equation of the new line in point-slope form will be:
y
- y1= 2(x
- x 1)
where (x 1, y 1) is any point on the new line.
Practice Problems, Point slope form worksheet algebra 1
Find the equation of the line that passes through the point (1, 2) and has a slope of 3.
Find the equation of the line that is parallel to the line y = x + 2 and passes through the point (3, 5).
Find the equation of the line that is perpendicular to the line y = -2x + 1 and passes through the point (2, 3).
Summary: Point Slope Form Worksheet Algebra 1
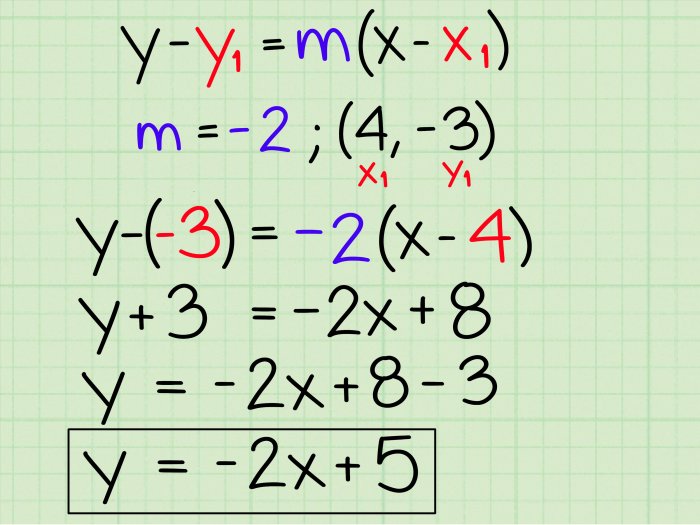
Point-slope form is a useful way to represent a linear equation. It is especially useful when you know a point on the line and the slope of the line. Point-slope form can be used to find the equation of a line that is parallel or perpendicular to a given line.
It can also be used to find the equation of a line that passes through two given points.
FAQ Summary
What is point-slope form?
Point-slope form is an equation for a line that is written in terms of a specific point on the line and the slope of the line.
How do I convert between point-slope form and slope-intercept form?
To convert from point-slope form to slope-intercept form, solve the equation for y. To convert from slope-intercept form to point-slope form, rearrange the equation so that it is in the form y – y1 = m(x – x1).
What are some real-world applications of point-slope form?
Point-slope form can be used to find the equation of a line that passes through two points, to find the slope of a line, and to graph a line.